Arm Confidential Computing Architecture (CCA) enables the creation of VM-based isolated execution environment.
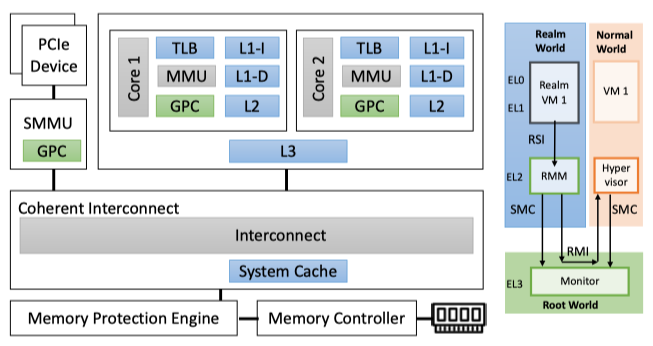
Blue: GPC enforcement
- When CPU core accesses memory: access control checks by the MMU
- When PCIe device accesses host memory: SMMU perform access control
- CCA ensures that the GPCs on MMU and SMMU are in sync to reflect the latest state of access control rules at world granularity.
Worlds
- Each core can program the access mode of physical address ranges to be root, realm, secure, or normal world.
GPT
- Granule protection table (GPT) tracks which physical address belongs to which of the four worlds.
- Maintained in the main memory, and belongs to the root world
- Only the monitor can access and update them.
GPC
- All processing elements (cores, SMMU, caches, TLBs) are augmented with Granule Protection Checks (GPC)
Trusted firmware
- Trusted firmware, executing in the monitor, sets the world bit for the core when it performs a context switch.
RMM
- Realm Management Monitor executes in the realm world at EL2.
- Ensures mutually distrusting realm VMs are isolated by managing stage-2 translations from guest physical address (IPA) to host physical address (PA)
Physical attack
- Bus-level encryption + integrity protection
- Cannot tamper data when it resides in the main memory
MPE
- Memory Protection Engine encrypts data before storing and decrypts it on the way to the bus.
- Relies on MEC (Memory Encryption Contexts) extension which is a part of Arm CCA.
- Each realm VM is associated with a unique key.
Workflow
VM Creation
- Hypervisor creates the realm VM
- Trusted monitor updates the GPT to change memory pages from normal to realm world
- ⚠️ GPT changes trigger flushing of TLBs caches of all GPCs
- RMM checks validity and updates its stage-2 translation tables